This post is part of my Game Physics Series.
Dynamic AABB tree is a type of broadphase that is borderless, meaning that it does not impose a strict border limit as some other broadphases do, such as explicit grid and implicit grid.
It is very efficient in all aspects in terms of game physics, including ray casting, point picking, region query, and, most importantly, generating a list of collider pairs that are potentially colliding (which is the main purpose of having a broadphase).
In this post, I will explain how a dynamic AABB tree works and show you a sample implementation.
The Structure
First, let’s look at the basic concept of a dynamic AABB tree. From its name, you can already guess that it has something to to with storing AABB-related information in a tree structure, and it is dynamic at run time.
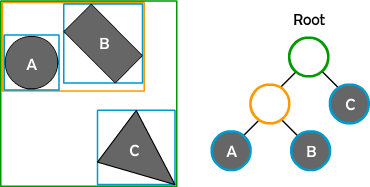
Each collider has its own AABB, and they are stored inside a binary tree as leaf nodes. Each internal node, a.k.a. branch node, holds its own AABB data that represents the union of the AABB of both of its children.
Visual aids are always better than plain text. The picture below shows a spatial configurations of several colliders and a visual representation of a possible corresponding tree structure.